In today’s competitive market, understanding the customer journey is paramount to successful marketing. A customer journey map visually outlines the process a customer goes through when interacting with your brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement. By building a comprehensive customer journey map, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, identify pain points, and optimize marketing strategies for improved customer experience and increased conversions. This article will guide you through the essential steps involved in crafting an effective customer journey map for marketing.
Creating a customer journey map is a crucial step in developing a customer-centric marketing approach. It allows you to walk in your customers’ shoes, understanding their motivations, frustrations, and expectations at each touchpoint. From the initial customer journey stage of awareness to the final stage of advocacy, this map serves as a blueprint for delivering personalized experiences that resonate with your target audience. Through a detailed customer journey mapping process, you can uncover opportunities to enhance customer satisfaction, build stronger relationships, and ultimately drive business growth. Learn how to build a powerful customer journey map that empowers your marketing efforts and strengthens your brand.
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
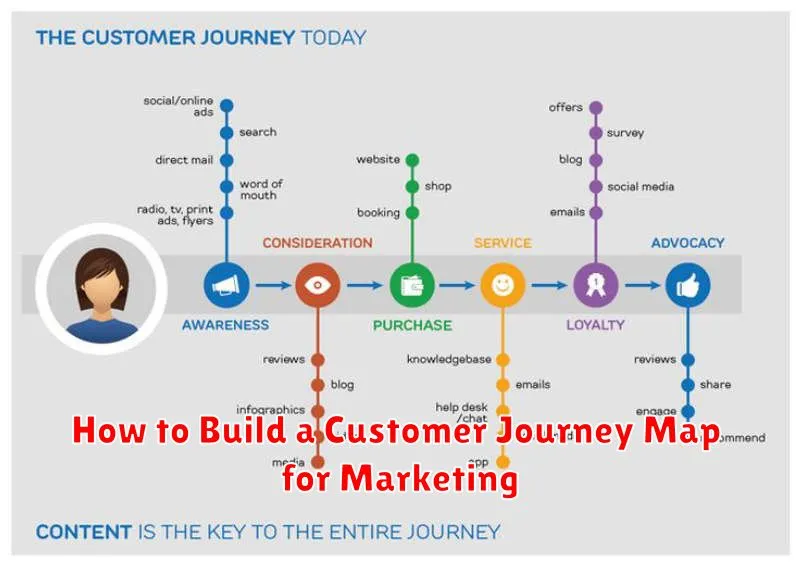
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the process a customer goes through when interacting with a company, product, or service. It outlines all the touchpoints a customer has with a business, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement.
This map helps businesses understand the customer’s perspective, identify pain points, and discover opportunities to improve the overall customer experience. It isn’t just a linear flowchart; it encompasses the customer’s emotions, motivations, and actions at each stage.
By mapping the customer journey, businesses can gain valuable insights into how customers interact with them, where they encounter friction, and what can be done to create a more seamless and positive experience. This understanding is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies and improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Identify Buyer Personas
Before mapping the customer journey, it’s crucial to understand who your customers are. This involves identifying your buyer personas. A buyer persona is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on market research and data about your existing customers.
Creating detailed buyer personas helps you understand your target audience’s needs, motivations, and pain points. This information is essential for tailoring your marketing messages and creating a customer journey map that resonates with them.
Consider these key aspects when developing your buyer personas:
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, education, income, etc.
- Psychographics: Values, interests, lifestyle, attitudes, etc.
- Professional Background: Job title, industry, company size, career goals, etc.
- Goals and Challenges: What are they trying to achieve? What obstacles are they facing?
- Information Sources: Where do they go for information (e.g., social media, websites, forums)?
Map Each Stage of the Journey
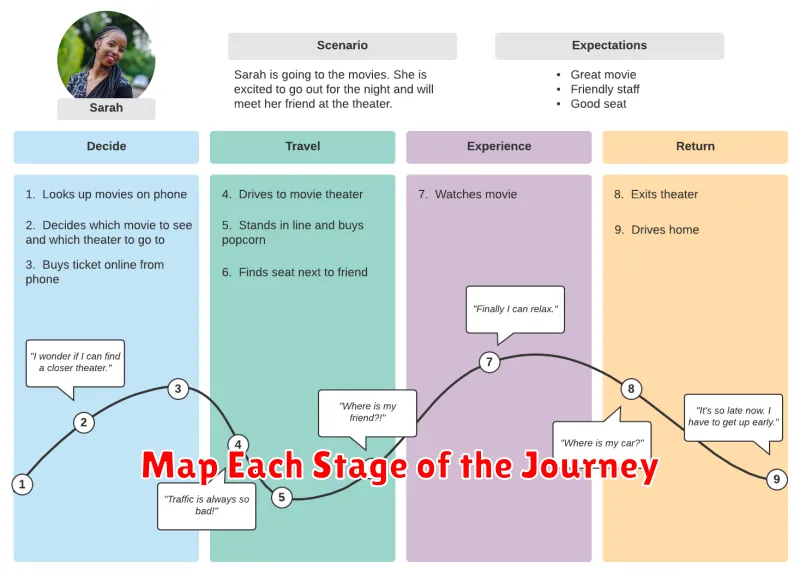
After identifying your target customer persona and outlining the touchpoints, the next crucial step is mapping each stage of their journey. This involves visualizing the customer’s experience from initial awareness to post-purchase interaction.
Common stages include Awareness (how do customers discover your brand?), Consideration (what factors influence their decision?), Decision/Purchase (what finalizes their choice?), and Post-Purchase (how do they interact with your product/service and brand after purchase?).
For each stage, define the customer’s actions, thoughts, and emotions. Understanding these aspects helps pinpoint potential pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Use Real Data and Feedback
A customer journey map grounded in reality relies on real data and genuine feedback. Avoid making assumptions. Instead, base your map on concrete evidence.
Data sources can include website analytics, CRM data, sales data, and market research reports. These provide quantitative insights into customer behavior.
Collecting feedback is crucial. Conduct surveys, interviews, and focus groups to understand customer perspectives. Social media listening can also provide valuable, unfiltered feedback.
By combining quantitative data with qualitative feedback, you create a robust and accurate representation of the customer journey.
Visualize Touchpoints Clearly
Touchpoints are crucial interactions between your customer and your brand. Clearly visualizing these interactions on your customer journey map is essential for understanding the customer experience.
Use distinct visual elements to represent different touchpoints. For example:
- Circles: could represent online interactions, like visiting your website or engaging with social media.
- Squares: could signify offline interactions, such as in-store visits or phone calls.
- Diamonds: might indicate key decision moments, like making a purchase or signing up for a service.
Maintain visual consistency throughout the map. A clear legend explaining the meaning of each symbol is also crucial for easy interpretation.
Consider the channel involved (website, email, social media, etc.) and the action taken by the customer (browsing products, adding to cart, contacting customer support). Clearly labeling each touchpoint with this information will provide valuable insights into the customer journey.
Analyze Pain Points and Gaps
After visualizing the customer journey, the next crucial step is to analyze pain points and gaps. Pain points are any negative experiences a customer encounters throughout their journey. These can range from complex website navigation to slow customer service responses. Identifying these friction points is essential for improving the customer experience.
Gaps represent discrepancies between the desired customer experience and the actual experience being delivered. These gaps can exist in various areas, such as communication, process, or product functionality. Analyzing gaps helps pinpoint areas where improvements are needed to better meet customer expectations and achieve business goals.
Look for patterns and trends in the collected data. Ask questions like: Where do customers most often abandon the journey? What are the most common complaints? Which touchpoints generate the most negative feedback? This analysis will provide valuable insights for prioritizing improvements and optimizing the customer journey.
Optimize Content for Each Stage
Once the customer journey stages are defined, tailor content to resonate with individuals at each specific point. This ensures maximum impact and encourages progression to the next stage.
Awareness Stage: Focus on educational content that addresses customer problems and introduces your brand as a potential solution. This might include blog posts, articles, or social media content that provides valuable information related to their needs.
Consideration Stage: Provide more specific content demonstrating your product or service’s value. Case studies, webinars, or product demos are effective formats for this stage. Highlight the benefits and features that address customer pain points.
Decision/Purchase Stage: Content at this stage should eliminate any remaining doubts and encourage conversions. Testimonials, free trials, or comparisons with competitors can help persuade potential customers to choose your offering. A clear call to action is crucial.
Retention/Advocacy Stage: Engage existing customers with content that fosters loyalty and encourages them to become brand advocates. This could include exclusive content, loyalty programs, or personalized recommendations.