A comprehensive SEO audit is crucial for maximizing your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). Understanding how to perform a complete SEO audit allows you to identify technical issues, on-page optimization opportunities, and off-page factors impacting your website’s performance. By conducting a thorough SEO website audit, you can uncover hidden obstacles preventing your site from ranking higher and attracting more organic traffic. This process involves a detailed analysis of various elements, from technical aspects like site speed and crawlability to content quality and keyword optimization. A well-executed SEO audit provides a roadmap for improving your online presence and achieving your business objectives.
This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to performing a complete SEO audit, covering all critical areas that influence your search engine rankings. From analyzing your website’s technical infrastructure and keyword research to evaluating your content strategy and backlink profile, we will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to conduct a comprehensive SEO audit. Whether you are a seasoned SEO professional or just beginning your journey, this guide will offer valuable insights and actionable strategies to boost your website’s SEO performance and drive organic growth.
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a comprehensive analysis of a website’s performance in organic search results. It’s a systematic evaluation that identifies technical issues, content gaps, and off-page factors that might be hindering a site’s visibility to search engines like Google.
Think of it like a health checkup for your website. The audit helps pinpoint areas needing improvement and provides actionable recommendations to enhance search engine rankings, drive more organic traffic, and ultimately, achieve business objectives.
A typical SEO audit covers several key areas:
- Technical SEO: Examines website infrastructure for crawl errors, indexing issues, and mobile-friendliness.
- On-Page SEO: Analyzes content quality, keyword optimization, and meta descriptions.
- Off-Page SEO: Evaluates backlinks, social media presence, and online reputation.
- User Experience (UX): Assesses site navigation, page speed, and overall usability.
Check Indexing and Crawlability
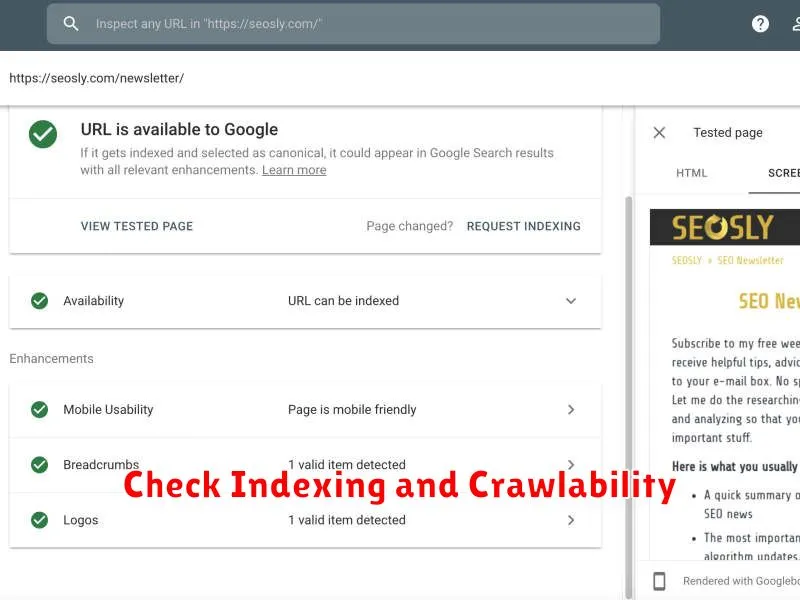
Ensuring search engines can access and index your website is crucial. This section focuses on verifying proper indexing and crawlability.
Index Status
Check how many of your pages are indexed by Google. Use the “site:” operator in Google Search (e.g., site:yourwebsite.com). A significantly lower indexed page count than expected indicates potential issues.
Robots.txt
Examine your robots.txt file. This file instructs search engines which parts of your site to crawl. Ensure it isn’t unintentionally blocking essential pages.
XML Sitemap
Verify your XML sitemap is submitted to Google Search Console. This provides search engines with a roadmap of your website, aiding in efficient crawling.
Crawl Errors
Within Google Search Console, review the Crawl Errors report. Address any 404 errors or other crawl issues promptly.
Analyze Site Structure and Navigation
A well-organized site structure is crucial for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO). Search engines need to easily crawl and understand your website’s content. Users need to be able to find what they are looking for quickly and efficiently. This section focuses on evaluating how well your site facilitates both.
Site Structure
Examine your site’s hierarchy. Is it logical and intuitive? A clear hierarchy, often visualized as a pyramid, helps search engines understand the relative importance of your pages. Ensure your most important pages are closer to the homepage.
Navigation
Navigation plays a key role in user experience and site crawlability. Your website’s menu should be clear, concise, and easy to use. Every page should be accessible within a few clicks from the homepage. Consider using breadcrumbs to help users understand their location within the site’s hierarchy.
XML Sitemap and robots.txt
Ensure you have an XML sitemap submitted to search engines. This file acts as a roadmap for search engine crawlers. Also check your robots.txt file. This file tells search engines which pages or sections of your website should not be crawled.
Review On-Page SEO Elements

On-page SEO refers to all the measures you can take directly within your website to improve its position in search rankings. A thorough review of these elements is crucial for a successful SEO audit.
Key on-page factors to analyze include:
- Title Tags: Ensure each page has a unique, concise, and descriptive title tag that accurately reflects the content.
- Meta Descriptions: While not a direct ranking factor, compelling meta descriptions can improve click-through rates from search results.
- Header Tags (H1-H6): Use header tags to structure your content logically and incorporate relevant keywords.
- Image Optimization: Use descriptive alt text for all images to improve accessibility and provide context to search engines.
- Content Quality: Focus on creating high-quality, informative, and engaging content that satisfies user intent.
- URL Structure: Keep URLs short, descriptive, and easy to understand.
- Internal Linking: Link relevant pages within your website to improve navigation and distribute link equity.
By carefully examining and optimizing these on-page elements, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility and search performance.
Test Site Speed and Mobile Friendliness

Site speed and mobile-friendliness are critical for SEO. Slow-loading websites negatively impact user experience and search engine rankings. Search engines prioritize websites that offer a seamless experience on all devices.
Use tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights to analyze your website’s performance. PageSpeed Insights provides a performance score and offers specific recommendations for improvement on both desktop and mobile. Focus on optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and minimizing HTTP requests.
Test your website’s mobile-friendliness with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool. This tool confirms whether your site adheres to mobile-first indexing best practices. A mobile-friendly website adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes, ensuring readability and ease of navigation for mobile users.
Inspect Backlink Profile
A thorough backlink audit is crucial for maintaining a healthy website and improving search engine rankings. Analyzing your backlink profile helps identify both high-quality links that boost your authority and potentially harmful links that could negatively impact your SEO.
Key aspects to examine include the number of backlinks, the quality of referring domains, and the anchor text distribution. A large number of backlinks from low-quality or spammy websites can harm your rankings. Similarly, an over-optimized anchor text profile can trigger penalties.
Utilize backlink analysis tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of your link profile. These tools can help identify toxic backlinks that should be disavowed. Disavowing bad links tells search engines to ignore these links when evaluating your website.
Fix Technical Issues Found
After identifying technical SEO issues during your audit, the next crucial step is resolving them. Addressing these problems directly impacts your website’s visibility and performance in search engine results. Prioritize fixes based on their potential impact and ease of implementation.
Common technical SEO problems include crawl errors, broken links, slow page speed, duplicate content, and mobile-friendliness issues. Utilize tools like Google Search Console and website auditing software to pinpoint specific problem areas.
Crawlability and Indexability are paramount. Ensure search engines can access and index your website’s important pages. Verify your robots.txt file isn’t blocking essential content and submit your sitemap to Google Search Console.
Page Speed Optimization is vital for user experience and SEO. Compress images, leverage browser caching, and minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files to improve loading times.

